Summary: How to remove biofilm naturally from teeth with the benefits of zinc and black seed oil.
This article provides information on natural methods of removing biofilm from teeth. It details the benefits of using zinc and black seed oil as a way to reduce the risk of plaque buildup. Zinc helps reduce the production of bacterial acids that cause tooth decay, while black seed oil has anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties that can fight germs. The article also provides an explanation of why these methods are beneficial, and a few tips on how to include these ingredients into your oral hygiene routine.
Buy SPRINJENE natural toothpaste and get rid of Biofilm naturally!
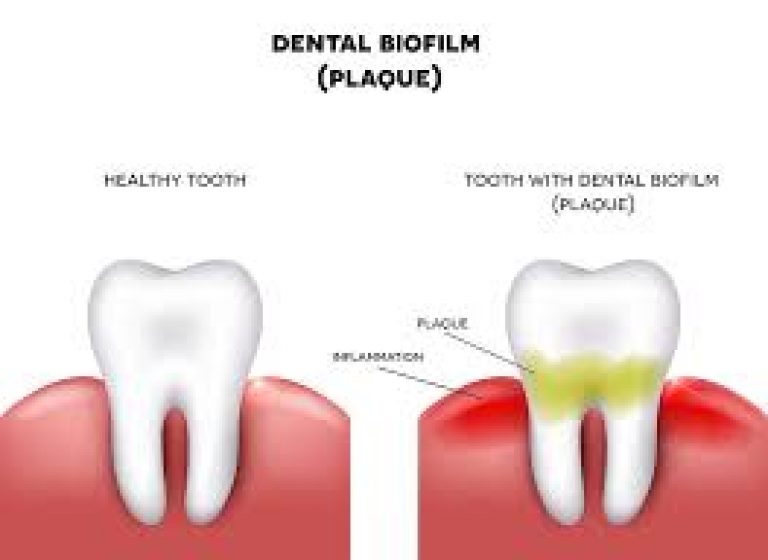
What is Biofilm?
Scientifically, the term ‘biofilm’ is used to describe the communities of micro-organisms attached to a surface. In simple terms, Biofilm occurs when bacteria present in a watery environment such as saliva begin to adhere to surfaces. These bacteria secrete sticky substances that attract more bacteria and lead to communities of disease causing microbes. Once they begin to multiply uncontrollably and accumulate they become associated with cavities and gum disease such as gingivitis and periodontitis.
See Sprinjene's All Natural Line of Black Seed Oil Toothpaste and Toothcare products here!
In the mouth, the biofilm appears as a yellowish buildup on the surfaces of teeth which may be removed by careful brushing, flossing and regular use of antibacterial mouth rinses. But underneath the tissues such as below the gum margin, physical removal of the biofilm may not be accomplished with a home care routine alone. This biofilm has now settled and become harder to form plaque and calculus, also known as ‘tartar’. Not only is it more stubborn but it also causes infection of the gums and surrounding tissues if left untreated. The tissues become inflamed and bleed, the pocket depths continue to increase and the pathogenic organisms become more and more harmful to the environment. . In addition, dental biofilm, especially sub gingival plaque in patients with periodontitis, has been associated with various systemic diseases and disorders, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, respiratory disease, and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
It has been identified that about 1000 different bacterial species are present in the dental biofilm.
Dental biofilm is primarily composed of micro-organisms which exist within an intercellular matrix that consists of organic and inorganic materials derived from saliva, the fluid present in the gingival crevices also known as crevicular fluid and bacterial products.
Clinical Implications:
It is important to understand the nature and pathophysiology of the dental biofilm to implement proper management strategies. Although the dental biofilm cannot be eliminated, it can be reduced and controlled by maintaining a proper oral health care regimen. Thorough mechanical oral hygiene procedures, including professional cleaning, tooth brushing and dental flossing are key to controlling biofilm accumulation. Since teeth make up only 20% of the mouth’s surfaces, for optimal oral health, the use of an antimicrobial mouth rinse helps to control biofilm not reached by brushing and flossing as well as biofilm bacteria present in the oral mucosa.
See Sprinjene's All Natural Line of Black Seed Oil Toothpaste and Toothcare products here!
Teaching patients to incorporate good quality dental products for brushing, interdental cleaning, and antimicrobial mouth rinses increases the likelihood of periodontal disease prevention and reduction.
Effects of Black Seed Oil and Zinc on Dental Biofilm:
Black seed oil clinical trials:
The Black seed or Nigella Sativa with thymoquinone as the main bioactive constituent is known to possess the following properties:
- Anti-inflammatory
- Anticancer
- Antioxidant
- Immunomodulation
- Antiglycemic
- Hepatoprotective
According to various studies and trials conducted it was found that both Black seed oil and thymoquinone have antibacterial effects on S. mutans within biofilms, and may therefore also have a deodorizing effect on the malodors produced by microbes. Black seed oil can safely be used for the prevention of oral malodor.
Based on the result of a present study, it can be concluded that N. sativa oil extract formulated in oil in water emulsion possesses antimicrobial activity against dental cariogenic bacteria. It further showed the potential use of this oil water emulsion to prevent and/ or cure common oral diseases such as gingivitis and periodontitis.
Effects of Zinc on dental biofilm:
Zinc is an essential trace element. In the mouth, it is present naturally in plaque, saliva and enamel. Zinc is added to oral health products to control plaque, reduce bad breath and inhibit calculus formation. It can maintain its substantivity in the oral cavity and elevated concentrations can persist for many hours in plaque and saliva after being delivered in to the mouth in the form of mouth rinses and toothpastes. Additionally, under certain conditions, low concentrations of zinc can enhance re-mineralization of enamel lesions, by slowing down lesion arrestment.
SprinJene Natural Toothpaste:
With both their anti-inflammatory, anti-cariogenic, anti-microbial, analgesic and immune boosting properties combined, it makes them ideal for use in oral formulations such as tooth pastes and mouth wash.
See Sprinjene's All Natural Line of Black Seed Oil Toothpaste and Toothcare products here!
SprinJene Natural ToothPaste combines both these ingredients in a patented formula suitable for adults and children developed by Dr. Sayed.
″Nigella Sativa extracts may be prepared by any method, provided the extraction process does not render the extract unsuitable for use in compositions. We are so proud of what we’ve accomplished. It’s a real breakthrough in oral care, and very effective. A natural antibacterial and antioxidant, Nigella Sativa extracts or oils when added to dentifrice compositions, the ability of the dentifrice composition to lubricate the mouth tissues and/or treat dry mouth is enhanced. Moreover, the synergistic interaction of Black Seed and Zinc in Sprinjene toothpaste can address the disruption of oral biofilm and hence helps in reducing gingivitis that causes gum inflammation and gum bleeding" says Dr. Sayed.
Along with its chemical free nature, which safely guarantees zero side effects, SprinJene also takes pride in its certifications which are:
Halal and kosher: Belief that people from all faiths should have access to good oral health care.
Gluten free: For people suffering from celiac disease as well as respecting those who choose a gluten free lifestyle.
Vegan: Ideal for those who choose a vegan lifestyle.
Cruelty free: Neither ingredients nor products have been subject to animal testing.
REFERENCES:
- Tatakis DN, Kumar PS. Etiology and pathogenesis of periodontal disease. Dent Clin Nam. 2005;49:491–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socransky SS, Haffajee AD. Dental biofilms: Difficult therapeutics target. Periodontol 2000. 2002;28:12–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindhe J, editor. 4th ed. Oxford, UK: Blackwell Publishing Company; 1998. Clinical Periodontology and implant dentistry book. [Google Scholar]
- Newman MG, Carranza FA, Takei H, Klokkevold PR, editors. 10th ed. USA: Elsevier Health Sciences; 2006. Carranzas clinical Periodontology book. [Google Scholar]
- [cited in 2010]. Available from: http://www.lww.com.
- Scheie AA, Petersen FC. The Biofilm Concept: Consequences for future prophylaxis of oral disease. Cri Rev Oral Bio
- Med. 2004;15:4–. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frias J, Olle E, Alsina M. Periodontal pathogens produce quorum sensing signal molecules. Infect Immun. 2001;69:3431–4. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Afseth J, Helgeland K, Bonesvoll P. Retention of Cu and Zn in the oral cavity following rinsing with aqueous solutions of copper and zinc salts. Scand J Dent Res 1983 91: 42–45.
- Cummins D, Creeth JE. Delivery of anti-plaque agents from dentifrices, gels and mouthwashes. J Dent Res 1992 71: 143– 149.
- Young A, Jonski G, Ro¨lla G. Inhibition of orally produced volatile sulfur compounds by zinc, chlorhexidine or cetylpyridinium chloride-effect of concentration. Eur J Oral Sci 2003 111: 400– 404.
- Segreto V A, Collins EM, D’Agostino R et al. Anti-calculus effect of a dentifrice containing 0.5% zinc citrate dihydrate. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 1991 19: 29–31.
- El-Dakhakhany M. Studies on the chemical constitution of Egyptian N. sativa L. seeds. Planta Medica. 1963;11:465–470. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1100266. [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Halawani E. Antibacterial Activity of Thymoquinone and Thymohydroquinone of Nigella sativa L. and Their Interaction with Some Antibiotics. Advances in Biological Research. 2009;3:148–152. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kokoska L, Havlik J, Valterova I, Sovova H, Sajfrtova M, Jankovska I. Comparison of chemical composition and antibacterial activity of Nigella sativa seed essential oils obtained by different extraction methods. J Food Prot. 2008;71:2475–2480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]